Exploring Nature’s Weirdest Survival Tactics
Nature is incredibly diverse and its’ ecosystems are swarming with living beings that have evolved greatly over time to adopt different roles in their respective environment. The animals possess some capabilities that are so unimaginable that they can be borderline surreal. These bizarre animal adaptations redefine biology and display to us the sheer genius touch of mother nature. From animals who are capable of surviving unbearable conditions or even those with the most bizarre features that serve as protective mechanisms, here are a few examples of strange adaptations in animals.
1. Tardigrades – The Invincible Space Travelers
Water bears, which have been alternatively called tardigrades, are small but tough animals. They are able to withstand unbelievable conditions which would kill almost any other living thing. They have the ability to survive harsh conditions. This incredible ability makes them one of the toughest creatures on the earth.

They can withstand the vacuum of space, extreme radiation, heat as high as 150 degrees Celsius (302 degrees Fahrenheit), and freezing temperatures as low as -272 degrees Celsius (-458 degrees Fahrenheit) by going into a state called cryptobiosis. Tardigrades do this by drying out and going into hibernation with no metabolic activity. They can endure that condition for years. Once the conditions become favorable, they are able to resurrect themselves.
2. Axolotl – The Master Regenerator
Axolotls are a kind of salamander that has the most incredible talent in the animal world: regeneration. Instead of simply healing with scars like most animals, axolotls are capable of regenerating completely intact appendages, as well as complicated structures like the entire spine, a heart, and bits of a brain.

Axolotls possess cells that are capable of differentiating. Amazingly, they are able to do this regeneration more than once in their lifetime without the new tissue being inferior in quality. Scientists are researching such regenerative capabilities so that they can develop treatments for injuries in humans.
3. Bombardier Beetle – Explosive Defense
The Bombardier beetle actually has one of the most amazing defense mechanisms in nature. It sprays a boiling hot, toxic chemical squirt from its abdomen when threatened. When the beetle is agitated, it mixes hydrogen peroxide and hydroquinone from two different tanks in its abdomen to produce a brutal chemical burst.
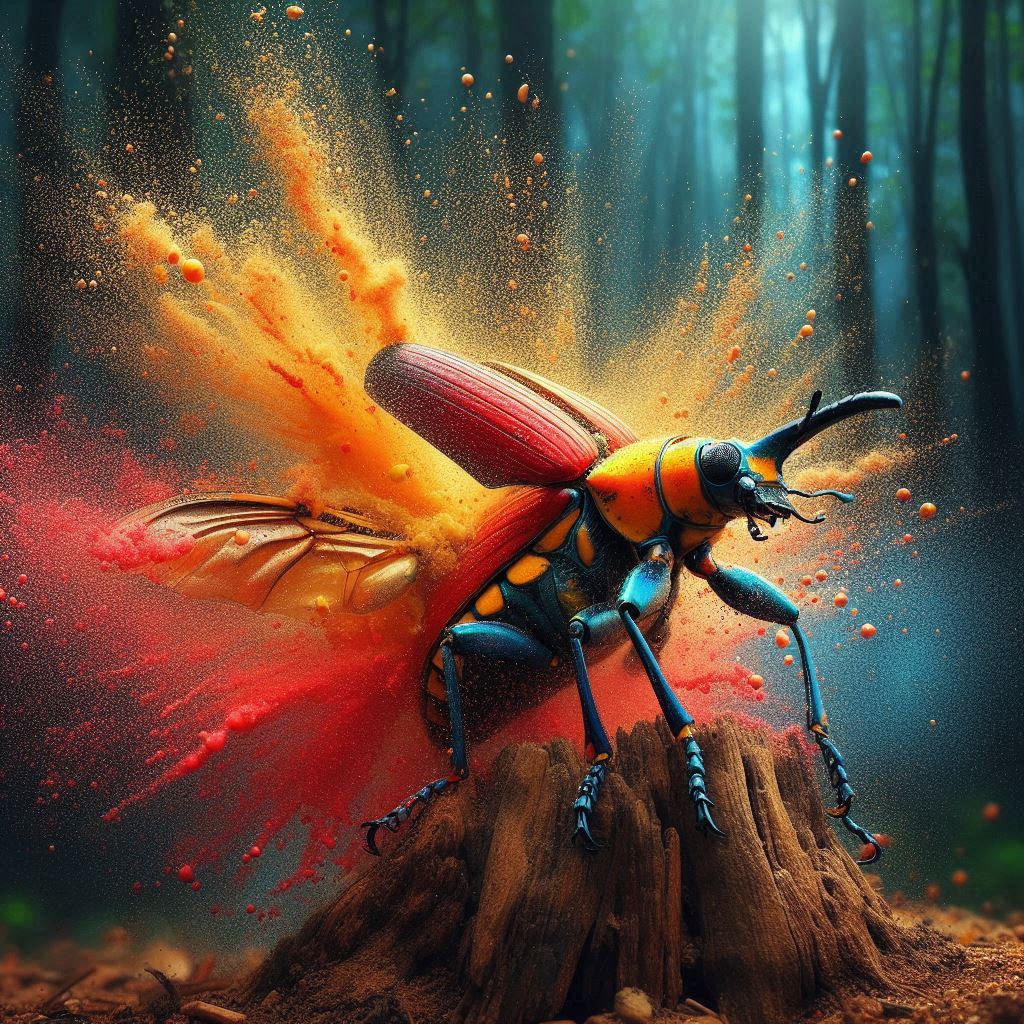

When threatened, these beetles mix the two chemicals causing a high-pressure chemical explosion reaching Aids hot (100°C / 212°F) that is explosively ejected towards any predators. The beetle is able to shoot this toxic spray in almost any direction and as such it serves as a formidable opponent for even larger animals. In a clever twist on chemical warfare, this is how the bombardier beetle protects itself in its natural habitat.
4. Mimic Octopus – Nature’s Shapeshifting Master
Mimic octopus (Thaumoctopus mimicus) is a type of shy cephalopod that camouflages itself in the dark waters of Southeast Asia. It can alter its body shape, color, and behavior to resemble other marine life. It can fan out its arms and display contrasting patterns, much like a poisonous lionfish, or it camouflages itself in the shape of an innocent flatfish that wanders along the seafloor. Imitating a sea snake, it conceals its body and leaves visible only two striped arms that wave like the snake’s body to dissuade predators.
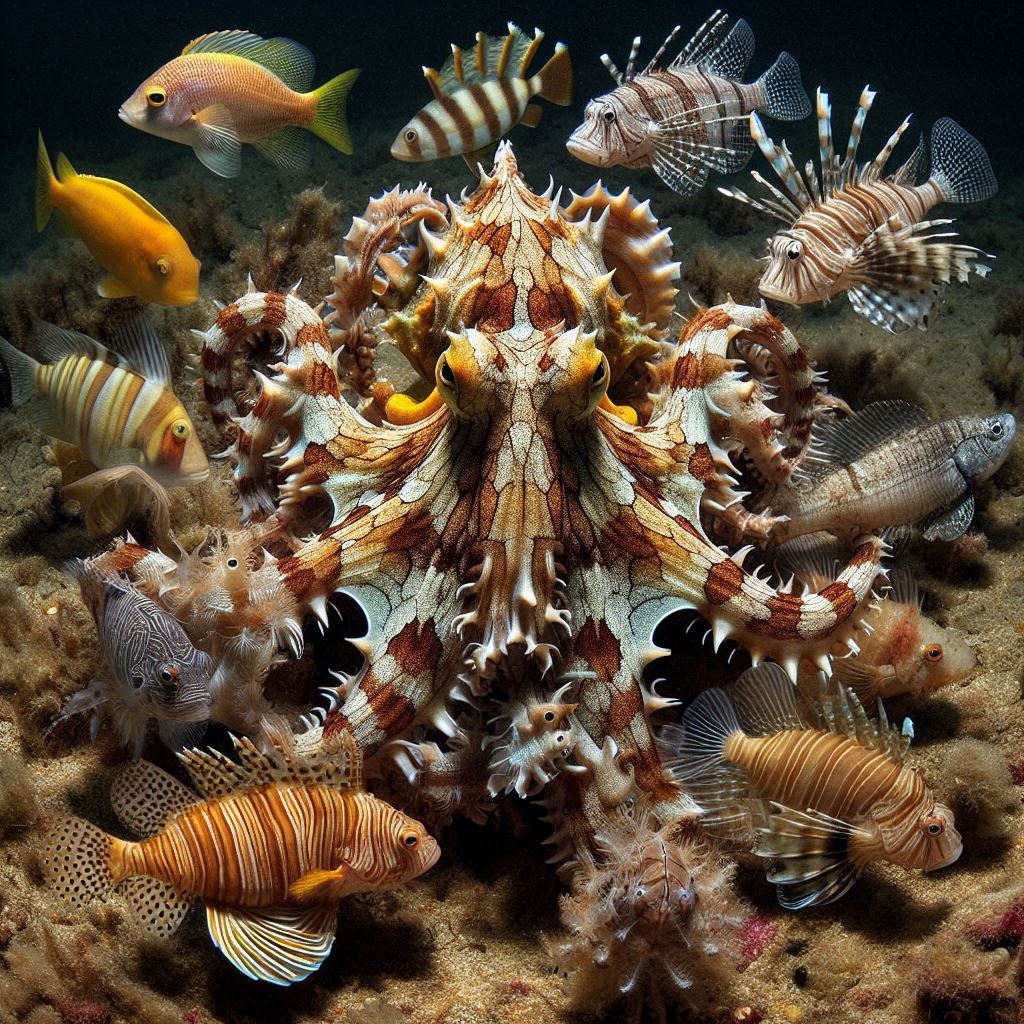

This form of mimicry is a survival strategy to confuse both the predator and the prey. This impressive skill allows them to camouflage and avoid predators in a very competitive environment.
5. Immortal Jellyfish – Turning Back Time
Turritopsis dohrnii is the Benjamin Button of jellyfish. After all, under duress — injury, starvation, or other environmental stresses — it merely reverts its adult cells to turn into baby ones. This process is called transdifferentiation and the jellyfish can potentially live forever.
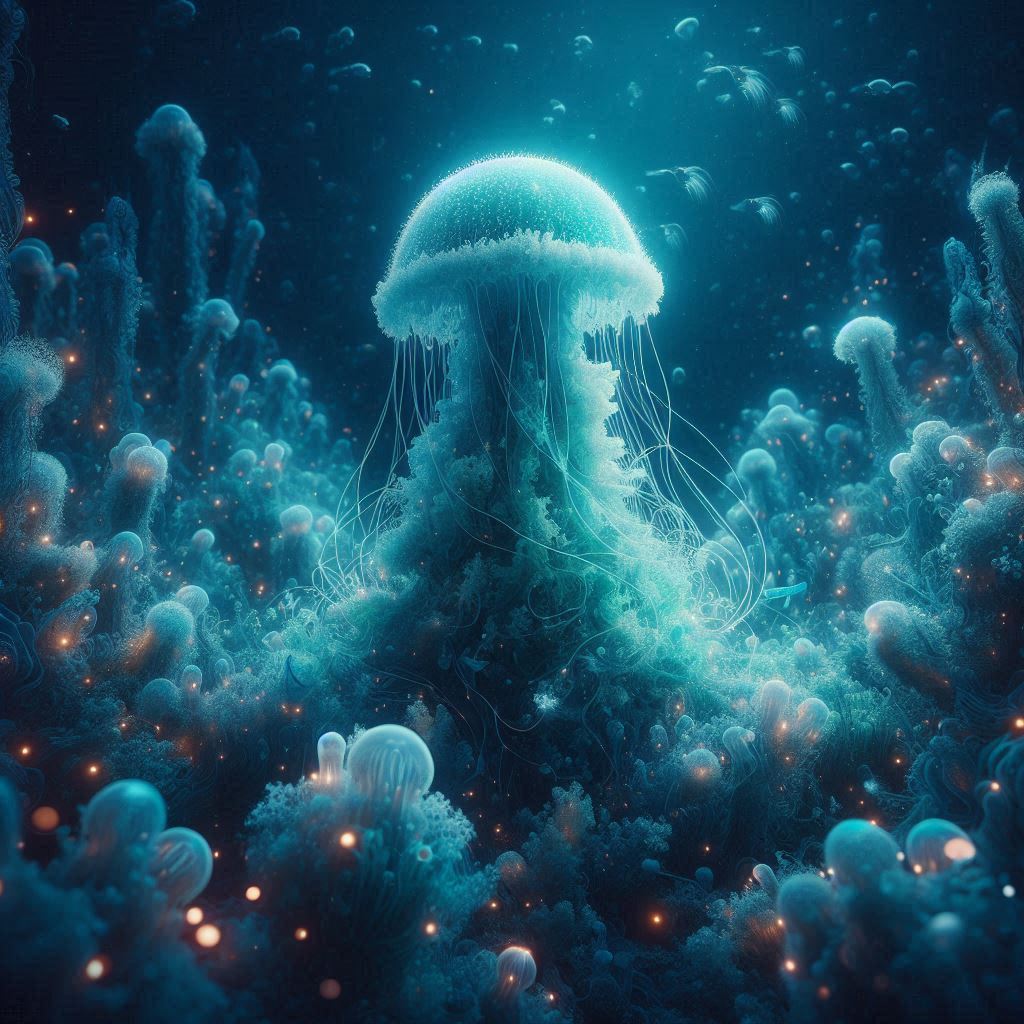

While they can still be devoured or killed by disease, the ability of immortal jellyfish to return from any age at will is a wonder of evolution. Scientists are paying close attention to it as they hope a better understanding of what happens in this species can help them learn more about how cells regenerate and age (in, say humans).
6. Pistol Shrimp – Wielding Nature’s Sonic Boom
The pistol shrimp has a powerful weapon in the form of its asymmetrical claws. It has a claw much bigger than the other and uses it as a high-speed sonic blaster. When the shrimp snaps that claw shut, the moving bubble travels at an incredible speed. Then the bubble crashes. It sends out a shockwave that can reach temperatures more than 5,000°C (9,000°F). Believe it or not, it’s hotter than the surface of the sun.
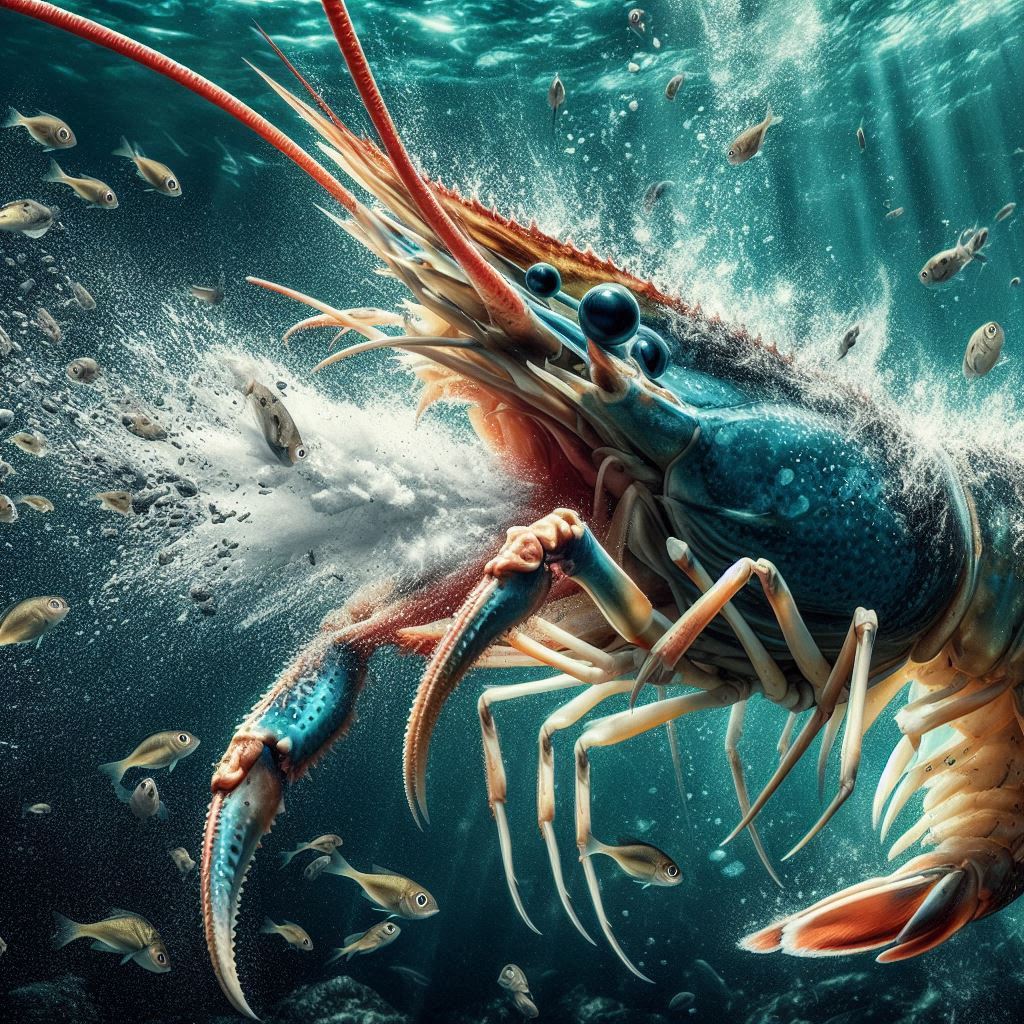

The shock is so powerful that it can stun small fish or crabs easily and sometimes even kill them. It also makes a really loud snapping sound just like a gunshot. This incredible ability makes the pistol shrimp one of the most fascinating animals of its size in the ocean.
7. Wood Frog – Frozen but Alive
The wood frog we see in North America has an amazing capability- during winter, it freezes solid. It’s so cold that its heart stops beating. It stops breathing. And furthermore, most of its body water freezes. Almost all the other animals would die at this point. However, the frog uses glucose and urea to prevent ice crystals from forming inside its cells. The process stops its cells from getting damaged. In this way, the frog can live being frozen for weeks or even months.
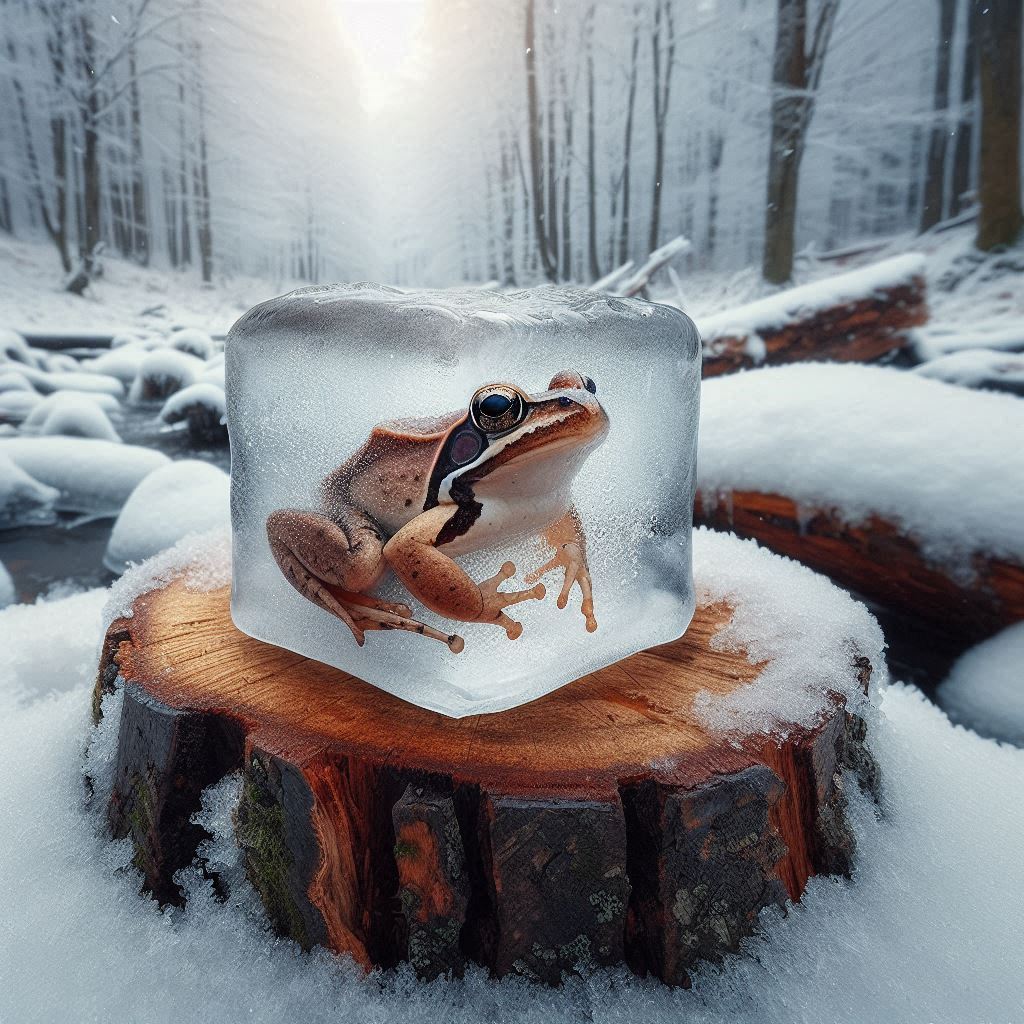

When the winter is over, the frog warms up. Its heart starts beating again. And it goes back to its normal activities, hopping around as if it hadn’t just spent months frozen in ice.
8. Sea Cucumber – Organ Sacrifice
The sea cucumber, when attacked by an animal can actually shoot their intestines out of their anus to lose/confuse the predator.

This procedure is called evisceration and it serves two purposes. The ejected organs serve as a distraction or food for the predator and the sea cucumber can flee the place. The other reason is that the sea cucumber is capable of regenerating its lost organs after a long period of time; this is a defense mechanism it can live through. It’s only two weeks, then back to normal, and they get to move on with life.
9. Platypus – Mammal with a Sixth Sense
Heck, even the Platypus, some freaky mammal from Australia that has a duckbill and webbed feet, but one of its more cool adaptations is that it can sense electromagnetic fields. The platypus can sense the electrical impulses from other animals moving around it.
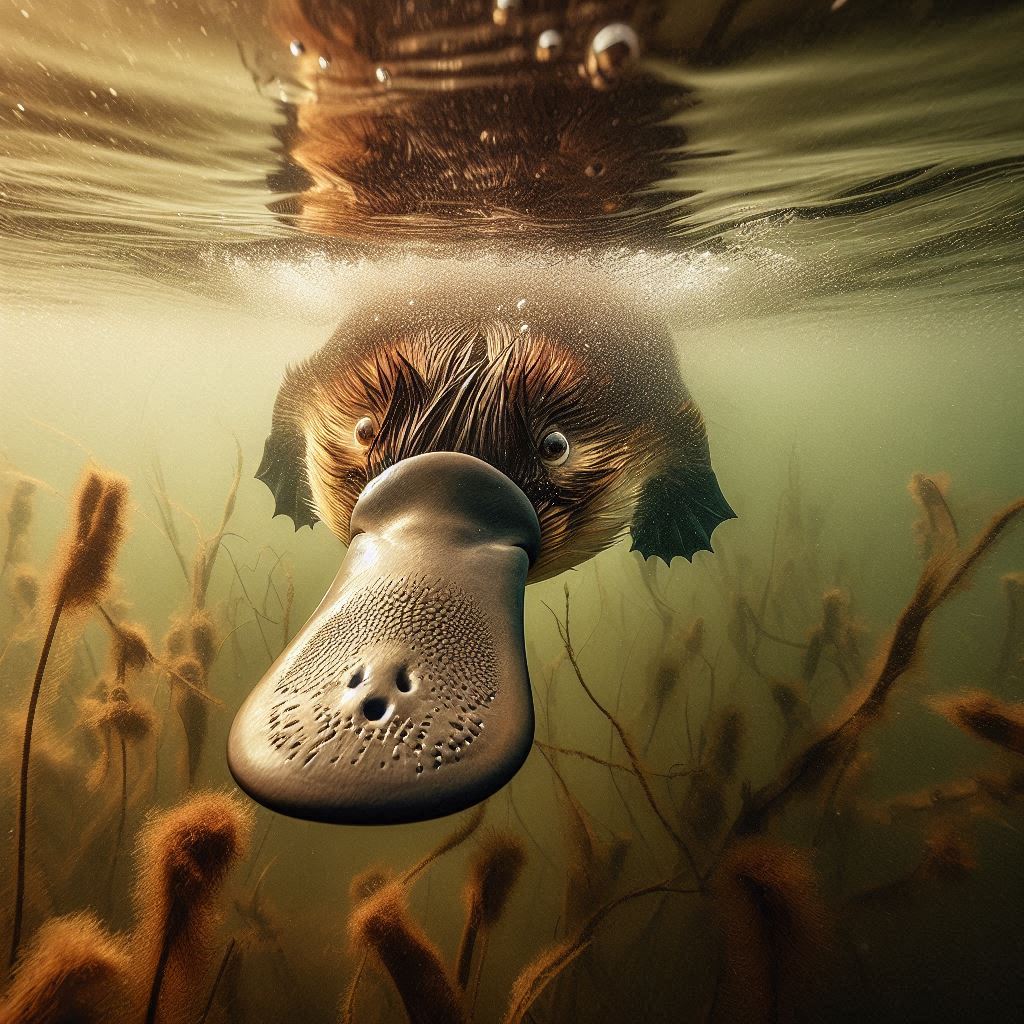

The process is called electroreception. It has electroreceptors in its bill. So it can hunt underwater even with its eyes, ears, and nose closed. This incredible ability allows the platypus to hunt shellfish and other small fish in the muddy water. This sixth sense gives the platypus a real advantage underwater.
10. Anglerfish – The Deep-Sea Lure
Anglerfish live in the deep, dark ocean. Female angler fish have developed a glowing trap which is known as esca. It’s a protrusion on top of their heads that glows as it has symbiotic bacteria inside. The light coming from this lure draws the prey and the anglerfish devours it with its massive jaws.
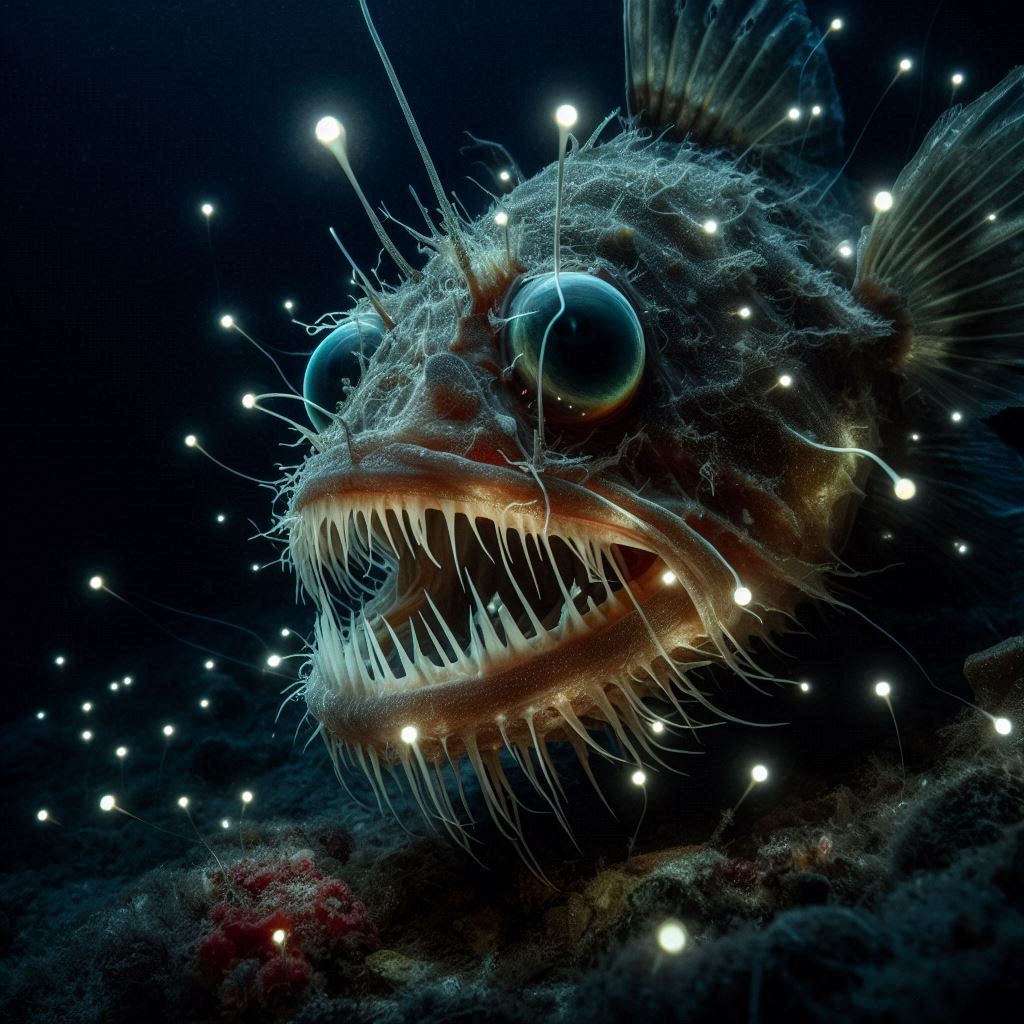

In the deep ocean, food is scarce. Due to this adaptation, angler fish survives as a predator. The surprising fact is that the male angler fish are tiny and latch onto their females and they just provide sperm when needed like gonads.
Lessons from Nature’s Most Bizarre Animal Adaptations
The vast animal world keeps on amaze us with their remarkable survival skills. They have adapted cleverly to thrive in the toughest environments. From the tiny tardigrades that can survive space to the platypus with its sixth sense underwater – nature is full of surprises with these bizarre animal adaptations. We can see the creativity of nature through these unique adaptations. From the very beginning of human civilization, we have taken inspiration from these adaptations. Studying these rare and unique qualities we have gained vast knowledge and have developed technology, medicine and have learnt sustainability.
Want to learn more interesting history about animals? Read our article about Strange Justice: Unraveling the Fascinating History of Animal Trials.